Learning Objectives
§ Carry out basic calculations on a project plan§ Understand the weaknesses of the CPM approach to planning and scheduling projects and recognise the need for alternative methods
Apply basic analysis to allow generation of buffered programmes
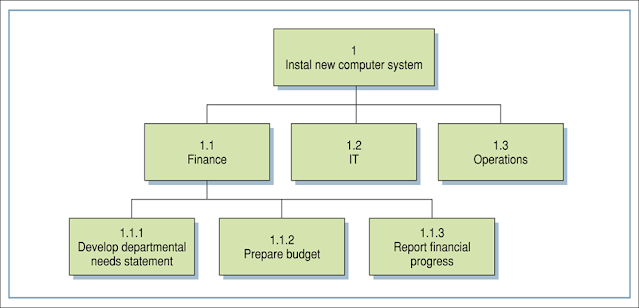
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
§ To create a linked, hierarchical series of activities that are comprehensible and manageable§ But not necessarily to be sequential
§ Projects can be broken down in a number of ways
§ Mostly activity oriented
Could also be functional or physical
A WBS Example: Activity Breakdown
§ Develop a PBS for a project in which you are going to build a bicycle. Try to identify all of the major components and provide three levels of detail.
Dealing with Increased Complexity in Scheduling
§ Many projects require a graphical method to analyse complex relationships among activities
§ Network diagram is such a method
§ In a network diagram activities can be represented as either
§ A node – known as activity-on-node (A-o-N)
§ An arrow – known as activity-on-arrow (A-o-A) - Not used in
Maylor (4th ed.)
Activity Time
![]()
Project start date 15/10
1.
Carry out literature review 15/10 – 25/11
2.
Arrange visits 26/11
– 9/12
3.
Design Experiments 10/12
– 30/12
4.
Review Experiments Design 31/12 – 20/1
5.
Conduct Experiments 21/1
– 17/3
6.
Analyse results 18/3
– 24/3
7. Write up 25/3
–18/4
Hand-in date 18/4
Plan in Graphical Form
Project start date |
1. Carry out literature review ******
2. Arrange visits **
3. Design Experiments ***
4. Review Design ***
5. Conduct Experiments ********
6. Analyse results *
7. Write up ****
Hand-in date |
15/10 26/11 10/12 31/12 21/1 18/3 25/3 18/4
Logical Links in Graphical Form - Gantt Chart
















0 comments:
Post a Comment